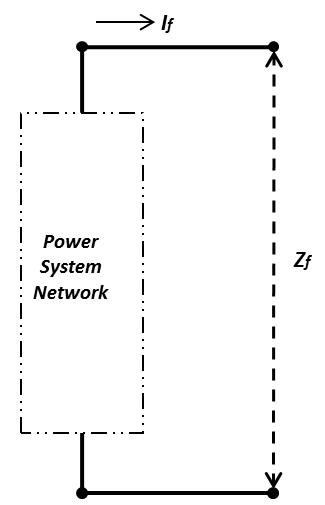
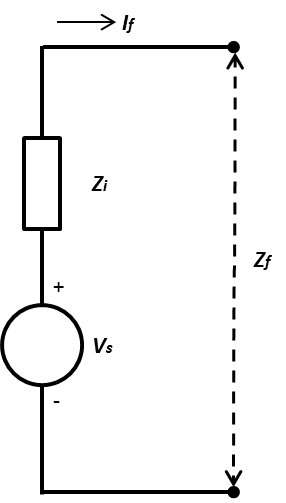
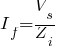Any power system network (Figure 1) can be represented by a simplistic Thevenin’s equivalent circuit (Figure 2). Using the Thevenin’s equivalent circuit of the network, it will be very easy to calculate the fault current at any point of the the power system.
where:
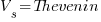 ‘
‘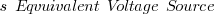
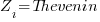 ‘
‘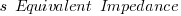
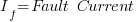
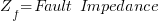
From Figure 2, the fault current will be
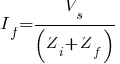
Most faults are considered to be bolted faults thus 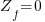 , which will simplify the equation to
, which will simplify the equation to